The headline in The New York Times (6/13/2013) was a little misleading, Study Gauges Value of Technology in Schools. The topic of gauging the value of technology is particularly significant given the investment by school districts everywhere in laptops, tablets, computer labs, Smartboards, whiteboards and projectors; but the article only referred to the use of technology in math or science.
The article by Motoko Rich referred to the “student survey data conducted in conjunction with the federal exams known as the National Assessment of Educational Progress,” This data was reviewed by the nonprofit Center for American Progress, which determined that middle school math students were using computers for math drills and other low level exercises. One of the more interesting points in the article noted that “no state was collecting data to evaluate whether technology investments were actually improving student achievement.” One of the problems noted in the report was the “lack of discrete learning goals” set by educators that results in the “use of devices in ways that fail to adequately serve students, schools, or taxpayers.”
When states do begin to collect data on the use of technology in the classroom, their studies should be broadened to include how technology is being used in other disciplines, specifically the language arts/English classrooms to facilitate writing. In contrast to reports of math and science technology use, language arts teachers are using a multitude of digital platforms to facilitate communication between students; technology offers opportunities for students to engage in formal and informal writing at every grade level.
Multiple digital platforms such as blogs or wikis allow students to post responses to questions posed by teachers. Students can share essays in order to peer edit or collaborate on projects, or students can follow links and create data in surveys and respond to the data created.
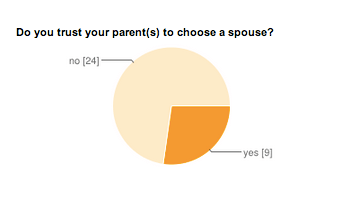 For example, an assignment for 9th grade students as part of a Romeo and Juliet unit to respond to a writing prompt can use multiple digital platforms to generate sophisticated responses. The assignment was posted on EDMODO and contained data from a student/parent survey on arranged marriages that students and their parents had completed on a Google Doc form. The survey results were posted on PBWorks for students to access for homework. Students needed to review the scene where Lord Capulet arranges Juliet’s marriage to the Count Paris before writing a response. Each response that was posted was available for the class to review and to discuss.
For example, an assignment for 9th grade students as part of a Romeo and Juliet unit to respond to a writing prompt can use multiple digital platforms to generate sophisticated responses. The assignment was posted on EDMODO and contained data from a student/parent survey on arranged marriages that students and their parents had completed on a Google Doc form. The survey results were posted on PBWorks for students to access for homework. Students needed to review the scene where Lord Capulet arranges Juliet’s marriage to the Count Paris before writing a response. Each response that was posted was available for the class to review and to discuss.
The assignment’s directions read:
The worldwide wide divorce rate for arranged marriages is 4%; this could be due to cultural taboos regarding divorce.
Look at the data on the page that you and your parents created.
What differences do you notice in your attitudes towards arranged marriages?
Now, Consider how the Capulet’s choice of Paris for Juliet may have been the better choice.
Was Romeo and Juliet’s choice to follow their passion the right decision?
Should they have followed their parent’s wishes?Respond in a well developed paragraph that includes:
- Introductory sentence that gives your opinion;
- evidence from the survey;
- evidence from R&J;
- Why this decision is important for future couples.
This assignment required a sophisticated analysis of data that the students had created, and an general analysis of characters from Shakespeare’s play.
Here are three responses generated by the prompt:
If Romeo and Juliet had listened to their parents almost all of this never would have happened. Even though just letting their parents choose would have solved everything, it was their decision. Romeo and Juliet had every right to choose their lives. Even the data from the survey shows that most children and parents don’t approve and less than 40% of people thought parents should choose. The Capulets didn’t know anything about their daughter and is trying to match her with someone who is completely wrong for her. This is why Eharmony uses Math equations because that is a lot more reliable than your parents.
In my opinion, Romeo and Juliet’s choice to follow their passion was the right choice. In the survey, some parents said that they could pick their child’s spouse. “I think I know my daughter well enough to know what kind of spouse she is looking for.” This parent has the same idea that Juliet’s did when they arranged for her and Paris to be married. Obviously in Juliet’s case, an arranged marriage did not work. She rebelled and went for Romeo. “Where is my Romeo?” was one of the first things Juliet said when she awoke from her sleep. Romeo and Juliet were love drunk and when they died they were both insanely happy. This is an important for future couples because if they’re in an arranged marriage it may end in death because one or both people are miserable.
I think that maybe Romeo and Juliet should have followed what their parents want. In our survey, 1/3 of the parents said they would be ok choosing their kid’s spouse, and 1/4 of us said that they would be ok with that. Romeo would still be in love with Rosaline, and he and Juliet would still be alive, their families would still be fighting but still they might have been happy. If Juliet haven’t meet Romeo she might have fallen in love with Paris, and who knows that if Romeo and Juliet were married they wouldn’t have divorced?
While there may be some question as to the effectiveness of technology in the classroom, the language arts/English classroom must be included in future studies by NAEP and in each state. There are multiple ways that digital platforms are being used to facilitate discussion and the sharing of ideas in language arts/English is far more sophisticated than the use of technology to “simply drill math problems.”